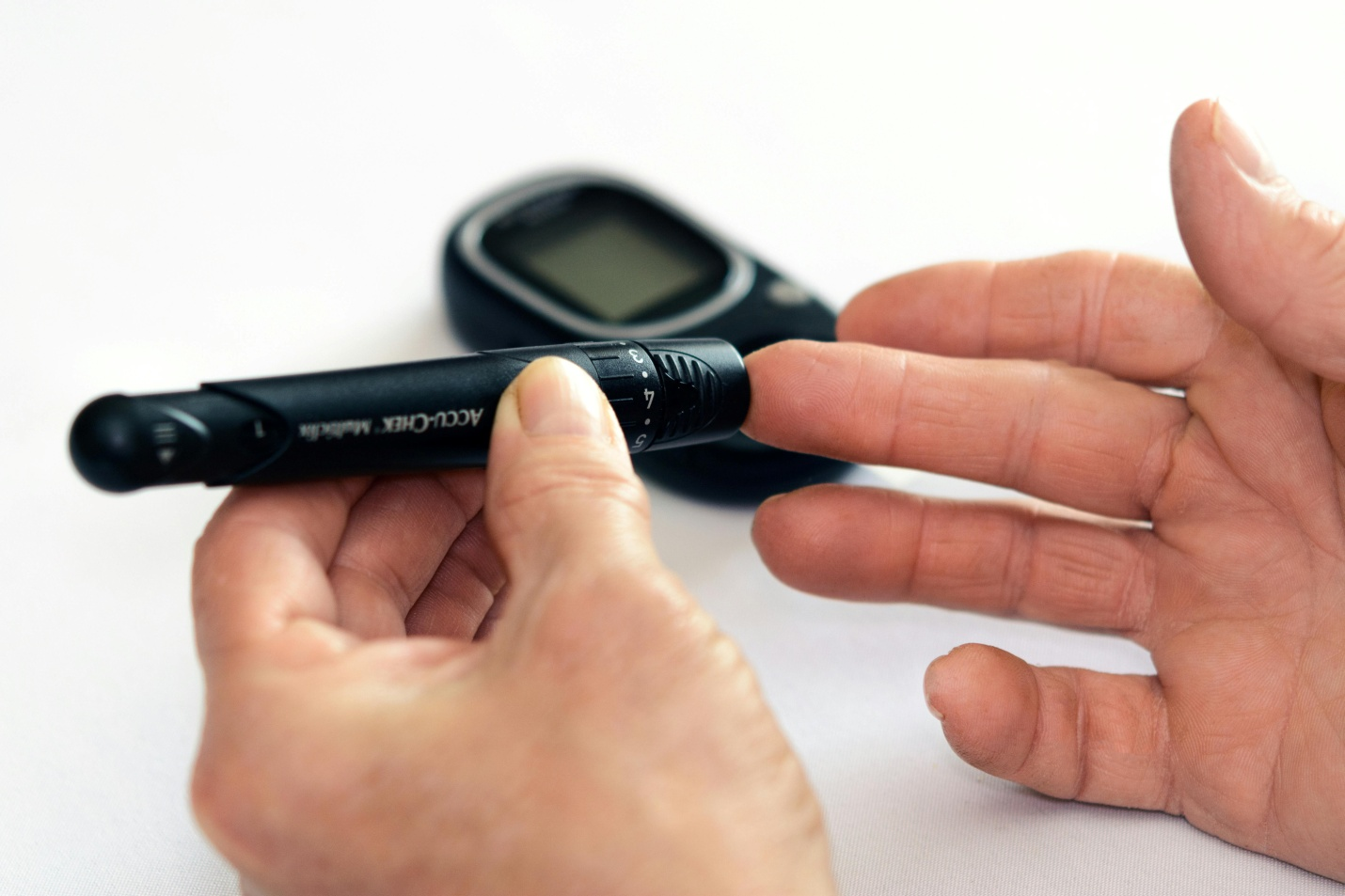
Managing Diabetes in Elderly
Diabetes is starting to become common in the older generations. Elderly need more medication and care as they get older. “In 1993, 41% of the 7.8 million people diagnosed with diabetes were over 65 years of age.”
Different doctors have variables of care and treatment. It is important for elderly to go to the doctor at least once a year for a check-up. Here is how to manage diabetes for the elderly.
The Effects of Aging
Problems that are related to age can affect those who already have diabetes. There are studies shown that half of the population over 65 years old has diabetes and is not aware of it. This is mainly due to the typical symptoms of hyperglycemia not being present from the physiological changes of aging.
Hyperglycemia creates a feeling of dehydration that is associated with diabetes. Another reason is very thirsty is a common occurrence in old age, and it is also a symbol that helps identify diabetes in people who do not know they have it yet.
Diabetes Diagnosis
Symptoms that are common with diabetes in elderly are changes in confusion and incontinence. Those who are lean and have type-one diabetes will experience diabetes differently. The symptoms will show similarly to younger patients who have type-one diabetes. Autoimmune changes may be displayed.
With obese elderly patients, the primary impairment is insulin resistant, in contrast to lean elderly that have impaired glucose-induced insulin release.
“Studies of healthy elderly patients have shown that glucose counterregulation involving glucagon, epinephrine, and growth hormone responses to hypoglycemia are diminished, which may contribute to the reduction in autonomic warning symptoms.9 Although classic overt symptoms of hypoglycemia may be absent, symptoms of cognitive impairment and long-term implications regarding dementia need to be researched.”
Changes in insulin and oral medications have to be made for diabetics based on age. The absorption and metabolism has to be taken into consideration. The doses also have to be factored in.
Complications are at higher rates the older the age. Some of the complications are nephropathy, erectile dysfunction, foot ulcers, and retinopathy. It is important for elderly to get their annual check up to help prevent any problems they might not be aware of.